Navigating Financial Standards
GAAP Principles & IFRS Rules
Explore GAAP Principles for rule adherence and IFRS Rules for global standards, merging precision and complexity in financial governance.
10 GAAP Principles
Principle of Regularity
GAAP-compliant accountants strictly adhere to established rules and regulations
Principle of Consistency
Consistent standards are applied throughout the financial reporting process
Principle of Sincerity
GAAP-compliant accountants are committed to accuracy and impartiality.
Principle of Permanence
Consistent procedures are used in the preparation of all financial reports.
Principle of Utmost Good Faith
All involved parties are assumed to be acting honestly.
Principle of Prudence
Speculation does not influence the reporting of financial data.
Principle of Continuity
Asset valuations assume the organization’s operations will continue.
Principle of Periodicity
Reporting of revenues is divided by standard accounting periods, such as fiscal quarters or fiscal years.
Principle of Materiality
Financial reports fully disclose the organization’s monetary situation.
IFRS Rules
- First-time Adoption of International Financial Reporting Standards
- Share-based Payment
- Business Combinations
- Insurance Contracts
- Non-current Assets Held for Sale and Discontinued Operations
- Exploration for and Evaluation of Mineral Resources
- Financial Instruments: Disclosures
- Operating Segments
- Financial Instruments
- Consolidated Financial Statements
- Joint Arrangements
- Disclosure of Interests in Other Entities
- Fair Value Measurement
- Regulatory Deferral Accounts
- Revenue from Contracts with Customers
- Leases
- Insurance Contracts
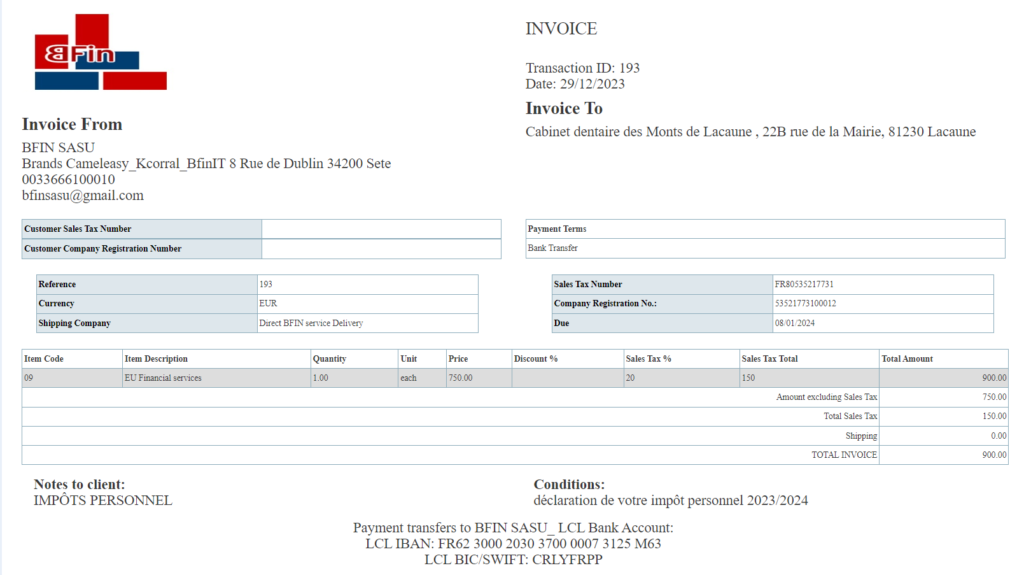
Invoice Sample Image
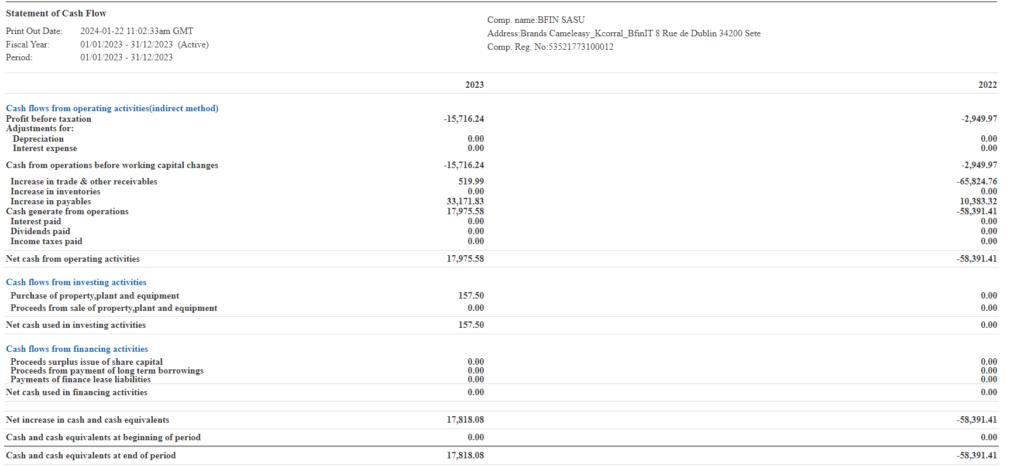
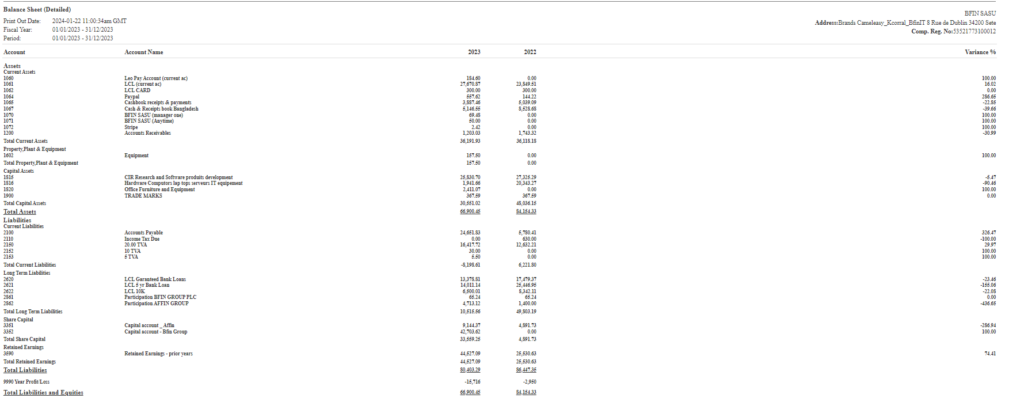
IFRS Report Sample Image